Thyroid Disease
Your thyroid (THY-roid) is a small gland found just below your Adam’s apple. It produces hormones that regulate the body functions. The thyroid hormones control the rate of many activities in your body such as how fast you burn calories and how fast your heart beats. All of these activities together are referred to as metabolism. The target when treating thyroid disease is to make sure that the thyroid that is working right by producing the right amounts of hormones needed to keep your body’s metabolism working at a rate that is not too fast or too slow.
Thyroid disorder: Who is affected?
Women are more likely than men to develop thyroid disorders. Most common thyroid disorders are Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism
Hyperthyroidism or Overactive thyroid:
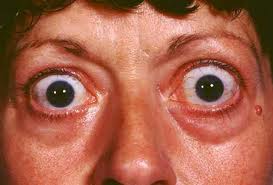
This when the thyroid is making more thyroid hormones than the body needs due to some disorders.
Sign& Symptoms: (***See you’re your care provider if you experience the following)
- Weight loss, even if you eat the same or more food; Eating more than usual
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat or pounding of your heart; Anxiety; Irritability; Trouble sleeping
- Trembling in your hands and fingers; Increased sweating
- Increased sensitivity to heat; Muscle weakness More frequent bowel movements
- More frequent bowel movements
- Less frequent menstrual periods with lighter than normal menstrual flow
- Exophthalmos – Bulging eyeballs
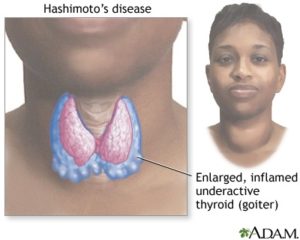
Hypothyroidism (hy-poh-THY-roi-diz-uhm) or Under active thyroid:
This is when your thyroid makes less thyroid hormone. In some cases, it is caused by treating hypothyroidism.
Signs & Symptoms: (***See your provider if you experience any of the following)
- Weight gain, even though you are not eating more food; Constipation
- Increased sensitivity to cold; Fatigue (feeling very tired); Depression
- Muscle weakness; Joint or muscle pain
- Pale dry skin; hair loss; A puffy face; A hoarse voice…
- Excessive menstrual bleeding…
Useful Link: http://womenshealth.gov/publications/our-publications/fact-sheet/thyroid-disease.cfm#a


